 |
Ramapo College Bioinformatics Group GRSDB - The 'G'-Rich Sequences Database |
| Search Help | Glossary of terms | Understanding G-Scores | Dealing with overlaps |
Glossary of the terms used in GRSDB
Term |
Definition |
G-Group |
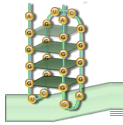
The set of G's that form the foundation for the G-quadruplex structure. There are four such groups in a quadruplex. Each group will be of the same size in a particular quadruplex, and in any case must contain at least two G's. |
Each QGRS is assigned a score based on a system (1)which rewards an arrangement of ‘G's that is likely to form a unimolecular quadruplex. For calculation of G-scores, the size and distribution of the gaps in the predicted QGRS is taken into consideration. Also, the larger size of the G-groups, the higher the score. For example, for a QGRS with G-groups of size two, the maximum possible score is 1. |
|
Gap or Loop |
The part of a QGRS that lies between two G-groups. For example, in the QGRS, (GG)GTA(GG)C(GG)TGA(GG), the four G-groups are in parentheses, so the three gaps are GTA, C, TGA. Note: up to one gap may be of length zero. |
GRS |
General term for a G-Rich Sequence. |
G-Quadruplex |
A three dimensional structure consisting of tetrads of G's connected by Hoogsteen bonds. Each tetrad is formed by taking one G from each G-group. The size of the G-group determines the number of tetrads found in the quadruplex. |
QGRS |
GRS that have the potential to form G-Quadruplex. The pattern for a QGRS is four groups of G's connected by arbitrary bases between each group. |
Near RNA Processing Sites |
A QGRS is defined to be near an RNA processing sites if it's starting position is within 120 nucleotides of the site. Exception: This distance is 150 nt downstream of a polyA signal |
Non-overlapping QGRS |
Two sequences are said to be non-overlapping if their positions in the nucleotide sequence do not overlap. The default action of GRSDB is to only display non-overlapping sequences (although the user can show all sequences if they choose). |
Overlapping QGRS |
Two QGRS are said to overlap if their positions in the nucleotide sequence overlap. Overlaps are eliminated by selecting for higher scoring sequence. |
1. D'Antonio,L. and Bagga,P.S. (2004) Computational methods for predicting intramolecular G-quadruplexes in nucleotide sequences. Computational Systems Bioinformatics, CSB 2004. Proceedings . 2004 IEEE, Pages:561-562.
| Search Help | Glossary of terms | Understanding G-Scores | Dealing with overlaps |